You are here: Urology Textbook > Urologic surgery > Lower midline incision
Lower Midline Incision: Surgical Steps and Wound Closure
Urologic Indications
In urology, a lower midline incision is used for an extraperitoneal approach to the prostate, bladder, distal ureters, and pelvic lymph nodes. In unexpected intraoperative findings, a lower midline incision can be easily extended.
Patient Positioning:
The patient is in a supine position with slight hyperextension of the lumbar spine.
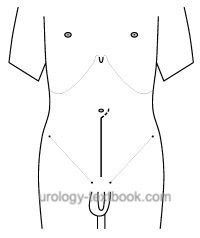 |
Surgical Technique of a Lower Midline Incision
- See fig. lower midline incision for the skin incision.
- Cut through the subcutaneous fat tissue and expose the rectus sheath
- Division of the linea alba and fascia transversalis. Blunt dissection of the Retzius' space.
- Using blunt dissection, the peritoneum is pushed superiorly and medially to expose the iliac vessels, spermatic cord and ureter. The posterior lamina of the rectus sheath may be divided to the umbilicus and further cranially for better exposure.
Wound Closure of Midline Incision
Wound closure is best done with the short stitch technique; continuous running suture (monofilament, elastic, slowly absorbable, suture size USP 0 or 2-0), tissue bites of 5 mm and intersuture spacing of 4–5 mm are applied exclusively to the fascia (linea alba) (Deerenberg et al., 2015). See also the section wound closure of transperitoneal midline laparotomy.
| Urologic Surgery | Index | Pfannenstiel incision |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
E. B. Deerenberg et al., “Small bites versus large bites for closure of abdominal midline incisions (STITCH): a double-blind, multicentre, randomised controlled trial.,” Lancet, vol. 386, no. 10000, pp. 1254–1260, 2015, doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60459-7.
J. A. Smith, S. S. Howards, G. M. Preminger, and R. R. Dmochowski, Hinman’s Atlas of Urologic Surgery Revised Reprint. Elsevier, 2019.
 Deutsche Version: Mediane Laparotomie
Deutsche Version: Mediane Laparotomie
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.
New release: The first edition of the Urology Textbook as an e-book—ideal for offline reading and quick reference. With over 1300 pages and hundreds of illustrations, it’s the perfect companion for residents and medical students. After your 7-day trial has ended, you will receive a download link for your exclusive e-book.