You are here: Urology Textbook > Adrenal glands > Adrenal incidentaloma
Diagnosis and Treatment of Adrenal Tumors (Incidentaloma)
Definition
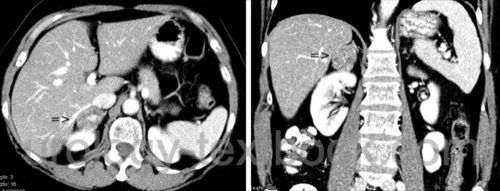
An adrenal incidentaloma is an (incidentally discovered) tumor of the adrenal gland. The most common cause is an adenoma without hormone production and without clinical significance. In 20%, a need for therapy arises from either progressive growth or hormone production.
 |
Pathology of Adrenal Incidentaloma
- Adenoma without hormonal activity (70%)
- Adenoma with cortisol secretion (10%)
- Adenoma with aldosterone secretion (6%)
- Pheochromocytoma (10%)
- Adrenocortical carcinoma (10%)
- Myelolipoma (8%)
- Cyst (5%)
- Ganglioneuroma (4%)
- Metastasis (7%)
Diagnosis of Adrenal Incidentaloma
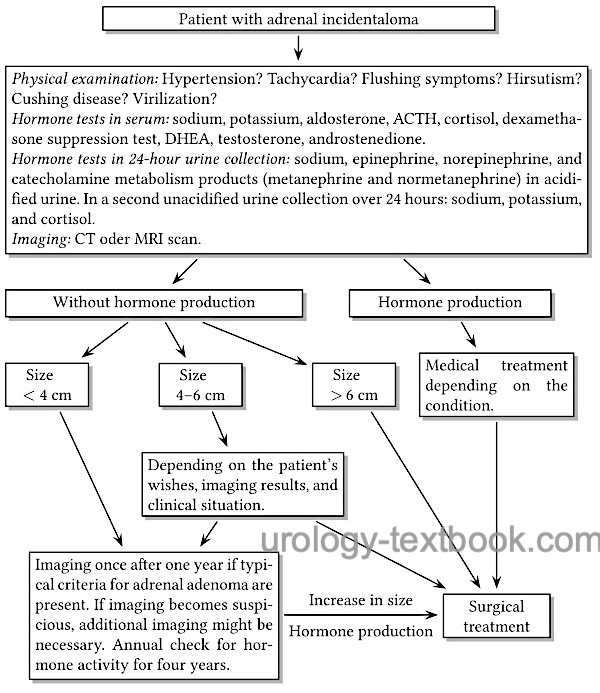
A rational diagnostic workup of incidentaloma is shown in the flowchart below.
 |
Physical examination:
Hypertension? Tachycardia? Flushing symptoms? Hirsutism? Cushing disease? Virilization?
Imaging:
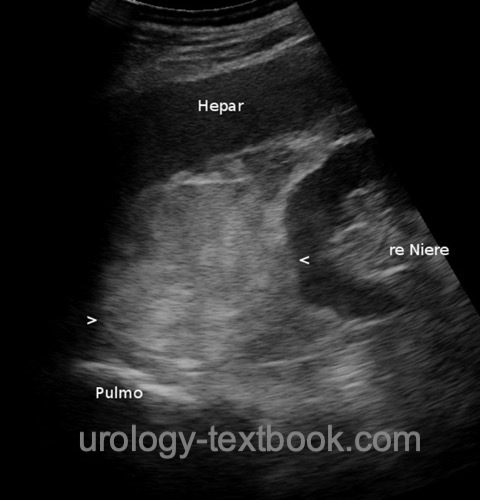
The diagnosis of an incidentaloma most commonly arises during imaging in case of complaints or during follow-up examinations of other diseases. CT characteristics of adrenal adenoma include evidence of fat in the tumor (native density of less than 10 HU); after contrast medium, adenomas typically enhance. 15 min after contrast medium, at least 60% of the enhancement should have disappeared. Contrast-enhancing lesions with native density values above 10 HU are suspicious for malignancy (Joudi et al., 2006). MRI is an alternative imaging technique and fat detection is possible with "chemical shift imaging"). For follow-up (size progression?), ultrasonography is also suitable.
 |
Hormone activity:
The hormone activity of adrenal tumor should be determined with blood tests and 24-hour urine collection:
- Serum: sodium, potassium, aldosterone, ACTH, cortisol, dexamethasone suppression test, DHEA, testosterone, androstenedione.
- 24-hour urine collection: sodium, epinephrine, norepinephrine, and catecholamine metabolism products (metanephrine and normetanephrine) in acidified urine. In a second unacidified urine collection over 24 hours: sodium, potassium, cortisol.
- Patients with hypertension: aldosterone/renin quotient in serum.
- Further tests depend on clinical suspicion and the results mentioned above.
Differential Diagnosis of Adrenal Tumors
- Adrenal adenoma
- Pheochromocytoma
- Adrenocortical carcinoma
- Rare benign tumors: hematoma, inflammatory tumors, ganglioneuroma, myelolipoma, lipoma, fibroma, adrenal cysts, oncocytoma.
- Neuroblastoma in children
- Lymphoma
- Metastases: mamma carcinoma, bronchial carcinoma, renal cell carcinoma, malignant melanoma, lymphoma.
- Tumors from neighboring organs such as kidneys, pancreas, spleen, bile ducts, vessels, and lymph nodes.
Active Surveillance and Treatment of Adrenal Tumors
A rational treatment for incidentaloma is shown in the flowchart above.
- Adrenal tumors <4 cm in size without hormone production: imaging once after one year if typical criteria for adrenal adenoma are present. If imaging becomes suspicious, additional imaging might be necessary. Annual check for hormone activity for four years. In case of size progression or hormone activity, adrenalectomy is indicated.
- Adrenal tumors 4–6 cm in size without hormone production: adrenalectomy or continue active surveillance (see tumors <4 cm size), depending on the patient's wishes, imaging results, and clinical situation.
- Adrenal tumors with hormone activity: adrenalectomy.
- Adrenal tumors larger than 6 cm: adrenalectomy.
| Adrenal insufficiency | Index | Pheochromocytoma |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
Barzon und Boscaro 2000 BARZON, L. ; BOSCARO,
M.:
Diagnosis and management of adrenal incidentalomas.
In: J Urol
163 (2000), Nr. 2, S. 398–407
M. Fassnacht et al., “European Society of Endocrinology clinical practice guidelines on the management of adrenal incidentalomas, in collaboration with the European Network for the Study of Adrenal Tumors.,” European journal of endocrinology, vol. 189, no. 1, pp. G1–G42, Jul. 2023, doi: 10.1093/ejendo/lvad066.
Joudi u.a. 2006 JOUDI, Fadi N. ; KUEHN,
David M. ; WILLIAMS, Richard D.:
Maximizing clinical information obtained by CT.
In: Urol Clin North Am
33 (2006), Aug, Nr. 3, S. 287–300
 Deutsche Version: Inzidentalom der Nebennieren
Deutsche Version: Inzidentalom der Nebennieren
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.
New release: The first edition of the Urology Textbook as an e-book—ideal for offline reading and quick reference. With over 1300 pages and hundreds of illustrations, it’s the perfect companion for residents and medical students. After your 7-day trial has ended, you will receive a download link for your exclusive e-book.