You are here: Urology Textbook > Drugs in Urology > Cephalosporins
Cephalosporins: Four Generations of Beta-Lactam Antibiotics
Four Generations of Cephalosporins
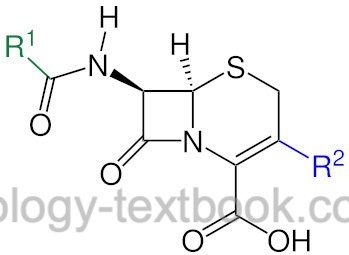
Cephalosporins are β-lactam antibiotics, which are grouped into four generations according to their antibiotic spectrum of activity (Simon and Stille, 1997). The first generation has mainly gram-positive activity. The second and third generation has more gram-negative activity with decreased activity against gram-positive bacteria. The fourth generation of cephalosporins has a broad spectrum of activity. The following list provides an overview of the generations of cephalosporins with significant substances:
- First generation: cefazolin, cefalexin, cefadroxil
- Second generation: cefamandole, cefoxitin, cefaclor, cefuroxime, loracarbef, cefotetan
- Third generation: cefotaxime, cefpodoxime, ceftizoxime, ceftriaxone, ceftazidime, cefoperazone
- Fourth generation: cefepime, cefozopran, cefpirome, cefquinome
Cefazolin
Antibiotic Spectrum of Cefazolin
Cefazolin is a first-generation cephalosporin. Cefazolin has a comparable antibiotic spectrum to penicillin. In addition, cefazolin has activity against gram-negative bacteria (E. coli, Klebsiella) and staphylococci.
Urologic Indications for Cefazolin
- Staphylococci infections
- Wound infections
- Perioperative antibiotic prophylaxis
- Cefazolin can replace penicillin for a penicillin allergy. Patients with penicillin allergy have a low risk of cross-allergy (10%), even lower with second and third-generation cephalosporins.
Pharmacokinetics of Cefazolin
Cefazolin is only for parenteral administration available. The elimination half-life is 1.5 h, with 90% renal elimination.
Side Effects of Cefazolin
- Allergy: 1–4%. Usually, there is a small risk for cross-allergy to a penicillin (10%)
- Allergic neutropenia
- Positive direct Coombs test, very rarely hemolytic anemia.
- Inhibiting the effect of anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents
Contraindications of Cefazolin
Cephalosporin allergy.
Dosage of Cefazolin
In adults, the dosage of cefazolin is 1 g 1-1-1 i.v. Children receive a daily dose of 60 mg/kg body weight, divided into three doses. Dose reduction is necessary for chronic kidney disease.
Second Generation of Cephalosporins
Cefuroxime, cefotiam, and cefaclor are essential substances of the second generation of Cephalosporins.
Antibiotic Spectrum of Second-Generation Cephalosporins
Good activity against streptococci, gonococci, meningococci, Haemophilus, and staphylococci. High β-lactamase resistance. No efficacy against Pseudomonas, enterococci, mycoplasma, and chlamydia.
Urologic Indications of Cefuroxime:
- Urinary tract infection
- Treatment of gonorrhea
- Staphylococci infections
- Surgical site infections
- Perioperative antibiotic prophylaxis
- Cefuroxime can replace penicillin for a penicillin allergy.
Pharmacokinetics of Cefuroxime and Cefotiam
Cefuroxime can be applied per os or intravenously. The elimination half-life is 1 hour with 70–90% renal elimination.
Side Effects of Cefuroxime
- Allergy: 1–4%. There is a minimal risk for cross-allergy to penicillin.
- Allergic neutropenia
- Positive direct Coombs test, very rarely hemolytic anemia.
- Inhibiting the effect of anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents
Contraindications of Cefuroxime
Cephalosporin allergy.
Dosage of Cefuroxime and Cefotiam
In urinary tract infections: cefuroxime 250–500 mg 1-1-1 p.o., 750 mg 1-1-1 i.v. or 1 g cefotiam 1-1-1 i.v., depending on the severity of infection Ovalle et al. 2000. Children receive 25 mg/kg i.v. 1-1-1. Double the dosage in severe infections. Dose reduction is necessary for renal insufficiency.
Third Generation of Cephalosporins
Important substances of third-generation cephalosporins are cefotaxime and ceftriaxone (cefotaxime-group).
Antibacterial Spectrum of cefotaxime and ceftriaxone
Cefotaxime and Ceftriaxone show good activity against streptococci, gonococci, meningococci, Haemophilus, and staphylococci. High β-lactamase resistance. Weak activity against Pseudomonas. No activity against enterococci, mycoplasma, chlamydia, and multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Urologic Indications for Third-Generation Cephalosporins
- Severe urinary tract infections: consider a combination with gentamicin to include enterococci.
- Severe postoperative infections like peritonitis: consider a combination with gentamicin to include enterococci.
- Treatment of gonorrhea: with a single intramuscular injection of ceftriaxone.
Pharmacokinetics of Cefotaxime and Ceftriaxone
Only parenteral administration of cefotaxime and ceftriaxone is possible. The elimination half-life is one hour for cefotaxime and 7–8 h for ceftriaxone. 50% renal elimination.
Side Effects of Cefotaxime and Ceftriaxone
- Allergy: 1–4%. There is a minimal risk for cross-allergy to penicillin.
- Allergic neutropenia
- Positive direct Coombs test, very rarely hemolytic anemia.
- Inhibition of the efficacy of anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents
- Alcohol intolerance possible
Contraindications
Cephalosporin allergy.
Dosage of Cefotaxime and Ceftriaxone
Treatment of severe infection: the daily dosage of cefotaxime in adults amounts to 3–6 g (children 50–100 mg/kg), depending on the severity of the infection, and is divided into three doses. The daily dosage for ceftriaxone is 2–4 g in two doses. Dose reduction is necessary with a renal insufficiency below a glomerular filtration rate of 5 ml/min.
Single shot treatment of gonorrhea: 250 mg ceftriaxone i.m. [see Chapter gonorrhea].
Oral Cephalosporins
Ceftibuten
Ceftibuten is an oral cephalosporin with high activity against Enterobacteriaceae. It is suitable for treating severe or complicated urinary tract infections in children Ho et al., 2001 Vilaichone et al., 2001.
Pharmacokinetics of Ceftibuten:
The elimination half-life is 2.5 h with 70% renal elimination.
Dosage of Ceftibuten:
400 mg 1-0-0 in adults, 9 mg/kg body weight 1-0-0 in children.
Cefixime
Cefixime is a derivative of cefotaxime, which can be given orally. Cefixime is suitable for treating urinary tract infections in children Gok et al., 2001 Ho et al., 2001.
Pharmacokinetics of Cefixime:
The elimination half-life is 2.5 h, only 20% renal elimination, high biliary excretion.
Dosage of Cefixime:
Adults 200 mg 1-0-1 or 400 mg 1-0-0 p.o., children 4 mg/kg body weight 1-0-1 or 8 mg/kg 1-0-0.
Cefpodoxime
Cefpodoxime is a derivative of ceftizoxime. Cefpodoxime is suitable for the oral treatment of urinary tract infections.
Pharmacokinetics of cefpodoxime:
The elimination half-life is 2.5 h with 30–40% renal elimination.
Dosage of cefpodoxime:
Adults 200 mg 1-0-1 and children 4 mg/kg body weight 1-0-1.
| Surgical management | Index | Pharmacology |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
Gok u.a. 2001 GOK, F. ; DUZOVA, A. ;
BASKIN, E. ; OZEN, S. ; BESBAS, N. ;
BAKKALOGLU, A.:
Comparative study of cefixime alone versus intramuscular ceftizoxime
followed by cefixime in the treatment of urinary tract infections in
children.
In: J Chemother
13 (2001), Nr. 3, S. 277–80
Ho u.a. 2001 HO, M. W. ; WANG, F. D. ;
FUNG, C. P. ; LIU, C. Y.:
Comparative study of ceftibuten and cefixime in the treatment of
complicated urinary tract infections.
In: J Microbiol Immunol Infect
34 (2001), Nr. 3, S. 185–9
Ovalle u.a. 2000 OVALLE, A. ; MARTINEZ,
M. A. ; WOLFF, M. ; CONA, E. ; VALDERRAMA, O. ;
VILLABLANCA, E. ; LOBOS, L.:
[Prospective, randomized, comparative study of the efficacy, safety
and cost of cefuroxime versus cephradine in acute pyelonephritis during pregnancy].
In: Rev Med Chil
128 (2000), Nr. 7, S. 749–57
Simon und Stille 1997 SIMON, C. ; STILLE, W.:
Antibiotika-Therapie in Klinik und Praxis.
9. Auflage.
Stuttgart New York : Schattauer, 1997
Vilaichone u.a. 2001 VILAICHONE, A. ; WATANA,
D. ; CHAIWATANARAT, T.:
Oral ceftibuten switch therapy for acute pyelonephritis in children.
In: J Med Assoc Thai
84 Suppl 1 (2001), S. S61–7
 Deutsche Version: Cephalosporine
Deutsche Version: Cephalosporine