You are here: Urology Textbook > Urologic examinations > Blood tests > Creatinine
Creatinine – Serum Blood Test
Creatine is an organic acid that helps to supply energy in skeletal muscles. Creatin is used (as creatine phosphate) to recycle ADP to ATP. Creatinine is a degradation product of creatine and is excreted by the kidneys. The renal elimination is mainly achieved by glomerular filtration, therefore, the creatinine concentration can be used to estimate renal function.
 |
Standard value:
Depending on age, muscle mass and laboratory test method: 0,6–1,4 mg/dl (50–130 μmol/l).
Laboratory test method:
The Jaffé reaction (colorimetric method with spectrophotometry) is less accurate than a specific enzymatic method or using standardized isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS).
Indications:
Routine test to measure renal function.
Differential Diagnosis of Elevated Creatinine Concentrations
- Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease.
- Non-renal causes of creatinine elevation are increased muscle mass, exsiccosis, meat-rich diet, high physical activity or laboratory artifacts, e.g., cephalosporins, acetylsalicylic acid, cyclosporin or bilirubin influence the Jaffé reaction.
- The following situations lead to low creatinine concentrations and may underestimate the extent of renal impairment: pregnancy, reduced muscle mass and low physical activity.
Creatinine Clearance and GFR
Renal excretion of creatinine is mainly dependent on the glomerular filtration rate. Since the intra-individual muscle mass remains relatively constant, the serum concentration of creatinine is a good marker for renal function. The serum concentration of creatinine also depends on factors such as drinking volume, physical activity, age and gender. The following formula (after Cockroft and Gault) is using the serum creatinine concentration in mg/dl (SCrea), gender (factor F=72 for men and F=85 for women), weight (in kg) and age (in years) to estimate the GFR (renal clearance):
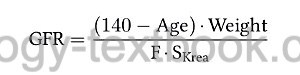 |
The MDRD formula is an alternative method to estimate GFR (from the Modification-of-Diet-in-Renal-Disease trial). The input of the formula is restricted to data from the laboratory software, factor F=1 for men and F=0.742 for women:
GFR = 186 × (SCrea)-1,154 × Age-0,203 × F
In case of discrepancies or doubts the GFR should be measured using a 24-hour urine collection or cystatin C.
| Phosphate in serum | Index | Cystatin C in serum |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
Guder, W. G. & Nolte, J. Das Laborbuch für Klinik und PraxisUrban + Fischer, 2009
Siegenthaler 1988 SIEGENTHALER, W. ; SIEGENTHALER, W. (Hrsg.): Differentialdiagnose innerer Krankheiten.
Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart, New York., 1988
 Deutsche Version: Kreatinin im Serum
Deutsche Version: Kreatinin im Serum
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.