You are here: Urology Textbook > Drugs in Urology > Alpha blocker > Doxazosin
Doxazosin: Side Effects and Dosage
- Alpha blockers: General pharmacology
- Alpha blocker Alfuzosin
- Alpha blocker Doxazosin
- Alpha blocker Silodosin
- Alpha blocker Tamsulosin
- Alpha blocker Terazosin
Mechanism of Action
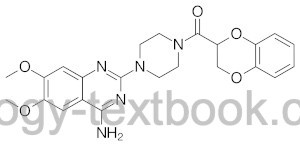
Doxazosin is a nonselective α1-blocker with long elimination half-life. Please see section general pharmacology of alpha blocker. Review Literatur: (Chapple, 2004).
 |
Indications for Doxazosin
- Treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic hyperplasia.
- Treatment of arterial hypertension
- Off-label treatment of female LUTS due to neurogenic bladder neck obstruction.
- Off-label treatment: improve the spontaneous passage of distal ureteral stones.
Pharmacokinetics of Doxazosin
Elimination half-life 22 h
Side Effects of Doxazosin
Increased side effect profile since doxazosin is a nonselective α1 blocker.
- Hypotension, orthostatic syncope, reflex tachycardia
- Stuffy nose
- Retrograde ejaculation
- Tachyphylaxis in the treatment of hypertension due to volume retention and peripheral edema.
- Dizziness, weakness
Contraindications of Doxazosin
Urological Contraindications:
Conservative treatment of BPH is not indicated, if surgical treatment is imperative: chronic urinary retention with renal failure, recurrent hematuria due to prostatic enlargement, recurrent infections and bladder stones.
Cardiac Contraindications:
Hypotension, mechanical heart failure (valvular, pulmonary embolism, pericarditis), congestive heart failure.
Other contraindications:
Doxazosin should be paused for cataract surgery to prevent an intraoperative floppy iris syndrome.
Dosage of Doxazosin
The treatment of doxazosin should be started with a low dosage, such as 1 mg orally once daily. The dosage can be increased each week to 2–4–8 mg orally once daily, depending on treatment effect, side effects and blood pressure. Doxazosin should be given before bedtime in the evening to reduce side effects.
| Terazosin | Index | Tamsulosin |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
Chapple 2004 CHAPPLE, C. R.:
Pharmacological therapy of benign prostatic hyperplasia/lower urinary tract symptoms: an overview for the practising clinician.
In: BJU Int
94 (2004), Nr. 5, S. 738–44
J. D. McConnell et al., “The long-term effect of doxazosin, finasteride, and combination therapy on the clinical progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia,” N Engl J Med, vol. 349, no. 25, pp. 2387–98, 2003.
 Deutsche Version: Doxazosin
Deutsche Version: Doxazosin