You are here: Urology Textbook > Urologic surgery > Gibson incision
Gibson Incision: Indications, Anatomy, and Surgical Steps
Urologic Indications
In urology, a Gibson incision is used for kidney transplantation or as an extraperitoneal approach to the distal ureter.
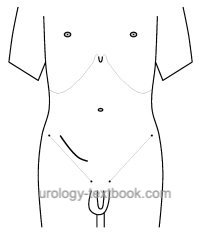 |
Patient positioning:
Supine position with slight hyperextension of the lumbar spine.
Surgical Technique of a Gibson Incision
- See fig. gibson incision for the skin incision.
- Divide the external oblique abdominal muscle in the direction of the muscle fibers.
- Transsect the internal oblique and transverse abdominal muscles at the lateral edge of the rectus sheath in the area of their aponeurosis. For a better approach, the lateral edge of the rectus muscle can be incised caudally.
- The inferior epigastric vessels are transected between ligatures.
- Push off the peritoneum cranially and medially with blunt dissection to expose the iliac vessels and ureter.
Wound closure:
Fascial closure in two layers with continuous running (monofilament, elastic, slowly absorbable, suture size USP 0 or 2-0) or interrupted sutures: the first suture reapproximates the internal oblique and transverse abdominal muscle, the second suture closures the external oblique abdominal muscle.
| Paramedian laparotomy | Index | Inguinal incision |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
J. A. Smith, S. S. Howards, G. M. Preminger, and R. R. Dmochowski, Hinman’s Atlas of Urologic Surgery Revised Reprint. Elsevier, 2019.
 Deutsche Version: Schräger Unterbauchschnitt nach Gibson
Deutsche Version: Schräger Unterbauchschnitt nach Gibson
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.