You are here: Urology Textbook > Surgery (procedures) > Internal urethrotomy
Internal Urethrotomy
Indications for Internal Urethrotomy
Internal urethrotomy is the first therapeutic option for short urethral strictures without pronounced scarring (Pansadoro and Emiliozzi, 1998).
Contraindications
- Untreated urinary tract infection
- Coagulation disorders
Surgical Technique of Internal Urethrotomy
Preoperative Patient Preparations
- Perioperative antibiotic prophylaxis: e.g., 2nd generation cephalosporin.
- Anesthesia: general or spinal anesthesia.
- Patient positioning: lithotomy position.
Direct-Vision Internal Urethrotomy
Direct-vision urethrotomy is the transurethral incision of the stricture under direct vision at 12 o'clock. The classic internal urethrotomy uses a cold knife [fig. internal urethrotomy]. Alternatively, the stricture is incised using a laser fiber (Nd:YAG or holmium). The incision of the urethral stricture should reach healthy tissue to minimize recurrent contraction of the scar.
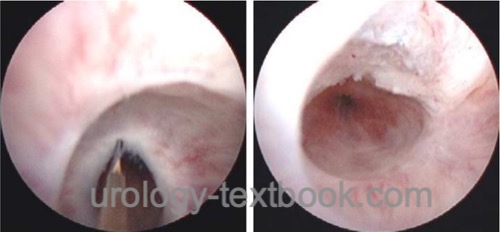 |
Blind Internal Urethrotomy (Otis)
An Otis urethrotomy is the blind transurethral incision of the urethra by an Otis urethrotome. After insertion of the Otis urethrotome, the urethra is dilated to the desired width and a blade cuts the stretched urethra at the 12 o'clock position.
The Otis urethrotomy is reserved for the palliative treatment of long-segment strictures of the male urethra or to treat proximal narrowing of the female urethra. Otis urethrotomy is also performed before the use of old resectoscopes (> 26 CH) in a narrow urethra to prevent ischemic damage. With modern 24 CH resectoscopes, this is rarely necessary.
Postoperative Management after Internal Urethrotomy
- Transurethral catheter for 2–7 days, depending on the stricture length. Long-term catheterization for up to six weeks did not produce better results. Recurrent urethral obturation (by the patient) is the better choice to prevent recurrent urethral stricture.
- Control micturition with urinary flow and residual urine
- Perioperative antibiotic treatment
Complications of Internal Urethrotomy
- Recurrence of the stricture, see section urethral stricture for details.
- Bleeding: deep cuts with injury of the corpus spongiosum or corpus cavernosum may lead to strong bleeding; they are managed by inserting an adequately sized catheter.
- Rare complications: erectile dysfunction due to injury of the erectile tissue, urinary incontinence due to injury to the urinary sphincter.
| Prostate Brachytherapy | Index | Anastomotic urethroplasty |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
Pansadoro und Emiliozzi 1998 PANSADORO, V. ;
EMILIOZZI, P.:
Die Urethrotomia interna.
In: Urologe A
37 (1998), S. 21–24
 Deutsche Version: Urethrotomia interna
Deutsche Version: Urethrotomia interna