You are here: Urology Textbook > Kidneys > Medullary sponge kidney
Diagnosis and Treatment of Medullary Sponge Kidney
Definition of the Medullary Sponge Kidney
A medullary sponge kidney is a congenital kidney malformation with cystic enlargement and calcification of the collecting ducts (Foster et al., 2007).
 |
Epidemiology:
- Symptomatic medullary sponge kidney: 1:5000 to 1:20000
- Asymptomatic medullary sponge kidney in urography: 1:200
Etiology:
In most sporadic cases, the exact cause of medullary sponge kidneys is unknown. In some patients, mutations can be detected in the RET (rearranged during transfection) and GDNF (glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor) genes; the patients may also show extrarenal malformations (Ria et al., 2017).
Pathology of the Medullary Sponge Kidney
The cut surface of the renal medulla looks like a sponge. The distal collecting ducts are dilated and have cysts with a diameter of 1–8 mm. Calcifications (70% calcium phosphate and 30% calcium oxalate) develop within the cysts. In 75%, medullary sponge kidney is bilateral.
Signs and Symptoms of a Medullary Sponge Kidney
- A medullary sponge kidney is often asymptomatic (incidental finding in urography or computed tomography)
- Recurrent nephrolithiasis
- Recurrent urinary tract infections
- Symptoms of chronic kidney disease (rare)
Diagnostic Workup of a Medullary Sponge Kidney
Ultrasound of the kidneys:
- Hyperechoic papillae
- Nephrolithiasis
Urography:
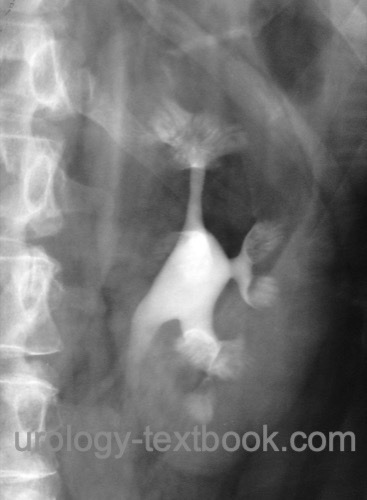
The contrast medium fills the ectatic collecting ducts, and the excretion is delayed: "paintbrush appearance" [fig. medullary sponge kidney in urography]. Progressive disease leads to calcifications in the distal collecting ducts: appearance suggestive of a "bouquet of flowers".
Differential Diagnosis of Bilateral Renal Calcification:
- Medullary sponge kidney
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Distal renal tubular acidosis
- Sarcoidosis
- Vitamin D intoxication
- Multiple myeloma
- Urogenital tuberculosis
- Milk-alkali syndrome
Treatment of the Medullary Sponge Kidney
Treatment in medullary sponge kidney is only necessary in complications like kidney stones, urinary tract infection or renal insufficiency.
Treatment of Nephrolithiasis:
Thiazide diuretics are suitable for the prevention of nephrolithiasis in nephrocalcinosis. Otherwise, the prevention and treatment of nephrolithiasis is similar to patients without medullary sponge kidneys.
Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections:
Frequent urinary tract infections with coagulase-positive staphylococci should be treated according to the urine culture results.
Prognosis of Medullary Sponge Kidney
In previous studies, the risk of renal failure in medullary sponge kidneys for symptomatic patients was 10%. Due to improved minimally invasive stone therapy options, this figure should be lower nowadays.
| Parapelvic cysts | Index | Kidney diseases |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
Forster, J. A.; Taylor, J.; Browning, A. J. & Biyani, C. S.
A review of the natural progression of medullary sponge kidney and a novel grading system based on intravenous urography findings.
Urol Int, 2007, 78, 264-269
 Deutsche Version: Markschwammniere
Deutsche Version: Markschwammniere
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.
New release: The first edition of the Urology Textbook as an e-book—ideal for offline reading and quick reference. With over 1300 pages and hundreds of illustrations, it’s the perfect companion for residents and medical students. After your 7-day trial has ended, you will receive a download link for your exclusive e-book.