You are here: Urology Textbook > Kidneys > Megacalycosis
Megacalycosis
Fundamentals and Symptoms of Megacalycosis
Definition:
Megacalycosis is the enlargement of the calyceal system without urinary tract obstruction or vesicoureteral reflux caused by a malformation of the renal papillae.
Epidemiology:
male:female = 6:1
Pathophysiology of Megacalycosis:
The malformation of the renal medulla leads to short collecting ducts and an increased number of calyces. Megacalycosis causes a mild disturbance of the maximum concentration capacity of the kidney, the long term prognosis in relation to renal function is good.
Signs and Symptoms:
In general, no complaints.
Diagnostic Workup of Megacalycosis
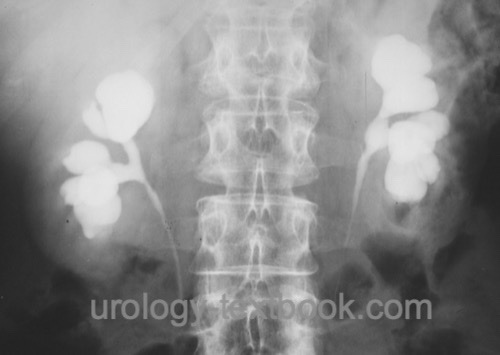
Intravenous Urography:
Intravenous urography shows an enlargement of the pyelocalyceal system and increased calyces. There is no ectasia of the renal pelvis and ureter [fig. Megacalycosis in intravenous urography].
VCUG:
No vesicoureteral reflux in voiding cystourethrography.
Renal Scintigraphy:
Renal scintigraphy reveals sormal renal function with rapid washout of the radionuclide.
 |
Treatment of Megacalycosis
Specific treatment is unnecessary.
| Calyceal Diverticulum | Index | Extrarenal calyces |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
 Deutsche Version: Megakalikose
Deutsche Version: Megakalikose