You are here: Urology Textbook > Urologic surgery > Pfannenstiel incision
Pfannenstiel Incision: Surgical Steps
Urologic Indications for a Pfannenstiel Incision
- Extraperitoneal surgical approach to the prostate, bladder, and distal ureters.
- The Pfannenstiel incision offers cosmetic advantages, but an extension in case of unexpected intraoperative situations is more complicated.
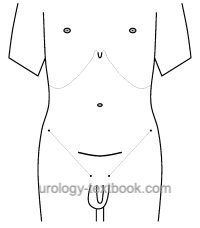 |
Patient Positioning
Supine position with slight hyperextension of the lumbar spine.
Surgical Technique of a Pfannenstiel Incision
- See fig. pfannenstiel incision for the skin incision .
- After exposure, the anterior lamina of the rectus sheath is divided 2–3 cm cranially of the symphysis. The lateral border of the rectus sheath should be seen.
- The anterior lamina of the rectus sheath is dissected off the rectus muscle to expose the midline between the rectus muscles. Caudally, the pyramidal muscles remain with the ventral lamina of the rectus sheath.
- Divide the midline and fascia transversalis to separate both rectus muscles. Now, a blunt dissection of the retropubic space (Retzius space) is possible. The peritoneum is dissected superiorly and medially to expose the iliac vessels, spermatic cord, and ureter.
Wound closure:
Interrupted sutures vicryl 0 are used to reapproximate the rectus muscle. Fascial closure is done with the short stitch technique: continuous running suture (monofilament, elastic, slowly absorbable, suture size USP 0 or 2-0), tissue bites of 5 mm and intersuture spacing of 4--5 mm are applied exclusively to the fascia (anterior lamina of the rectus sheath).
Wound closure:
Interrupted sutures vicryl 0 are used to reapproximate the rectus muscle. Fascial closure is done with the short stitch technique: continuous running suture (monofilament, elastic, slowly absorbable, suture size USP 0 or 2-0), tissue bites of 5 mm, and intersuture spacing of 4--5 mm are applied exclusively to the fascia (anterior lamina of the rectus sheath).
| Midline Incision | Index | Paramedian laparotomy |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
E. B. Deerenberg et al., “Small bites versus large bites for closure of abdominal midline incisions (STITCH): a double-blind, multicentre, randomised controlled trial.,” Lancet, vol. 386, no. 10000, pp. 1254–1260, 2015, doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60459-7.
J. A. Smith, S. S. Howards, G. M. Preminger, and R. R. Dmochowski, Hinman’s Atlas of Urologic Surgery Revised Reprint. Elsevier, 2019.
 Deutsche Version: Pfannenstiel Zugang
Deutsche Version: Pfannenstiel Zugang