You are here: Urology Textbook > Drugs in Urology > Alpha blocker > Silodosin
Alpha blocker Silodosin: Side Effects and Dosage
- Alpha blockers: General pharmacology
- Alpha blocker Alfuzosin
- Alpha blocker Doxazosin
- Alpha blocker Silodosin
- Alpha blocker Tamsulosin
- Alpha blocker Terazosin
Mechanism of Action of Silodosin
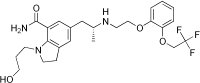
Silodosin is a selective alpha1A-blocker with a long half-life and favorable cardiovascular side effects (Cantrell et al., 2010). Please see section general pharmacology of alpha blocker.
 |
Indications for Silodosin
- Treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic hyperplasia.
- Off-label treatment of female LUTS due to neurogenic bladder neck obstruction.
- Off-label treatment: improve the spontaneous passage of distal ureteral stones.
Pharmacokinetics of Silodosin
Bioavailability 32%, high plasma protein binding, hepatic metabolization, elimination half life 13 h, biliary and renal excretion of metabolites.
General Side Effects of Alpha Blocker
Decreased side effect profile since silodosin is a selective α1A blocker.
- Hypotension, orthostatic syncope, reflex tachycardia
- Stuffy nose
- Retrograde ejaculation
- Dizziness, weakness
- Overall rate of side effects is between 10–30%.
Contraindications of Silodosin
Urological Contraindications:
Conservative treatment of BPH with silodosin is not indicated, if surgical treatment is imperative: chronic urinary retention with renal failure, recurrent hematuria due to prostatic enlargement, recurrent infections and bladder stones.
Cardiac Contraindications:
Hypotension, mechanical heart failure (valvular, pulmonary embolism, pericarditis), congestive heart failure.
Other contraindications:
Silodosin should be paused perioperatively for cataract surgery to prevent an intraoperative floppy iris syndrome.
Specific Contraindications of Silodosin
- Severe chronic kidney disease (<30 ml/min)
- Not approved in children.
- Inhibitors of CYP3A4 like ketoconazol
Dosage of Silodosin
8 mg orally once daily. Reduce dosage to 4 mg in patients with renal insufficiency (<50 ml/min).
| Alfuzosin | Index | Pharmacology |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
Cantrell, M. A.; Bream-Rouwenhorst, H. R.; Hemerson, P. & Magera, J. S. Silodosin for benign prostatic hyperplasia.Ann Pharmacother, 2010, 44, 302-310.
Chapple 2004 CHAPPLE, C. R.: Pharmacological therapy of benign prostatic hyperplasia/lower urinary tract symptoms: an overview for the practising clinician.
In: BJU Int
94 (2004), Nr. 5, S. 738–44
 Deutsche Version: Silodosin
Deutsche Version: Silodosin