You are here: Urology Textbook > Kidneys > Simple renal ectopia
Simple Renal Ectopia
Definition of Simple Renal Ectopia
Simple renal ectopia is the abnormal position of the kidney outside of the renal fossa in a cranial or caudal direction.
Location (from cranial to caudal):
- Thoracic kidney: position of the kidney above the diaphragm in the posterior mediastinum. The kidney is separated from the pleural cavity by a thin membrane in the continuity of the diaphragm.
- Normal kidney position: in the renal fossa.
- Lumbar position: location in the iliac fossa.
- Pelvic kidney [fig. tomography of a pelvic kidney]: position of the kidney below the aortic bifurcation.
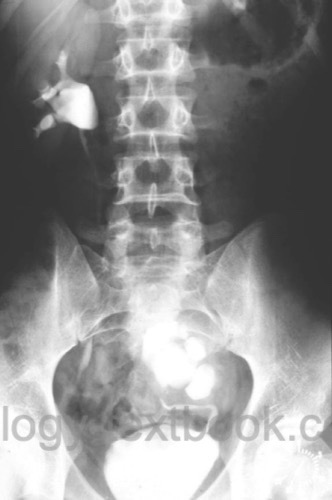 |
Epidemiology of simple renal ectopia:
1:500 to 1:1200, slightly more often on the left side.
Causes (Etiology) of Renal Ectopia
Renal ectopia is caused by a disorder of renal ascension. Genetic or teratogenic causes are probable due to frequent coexisting genital abnormalities. The renal pelvis is often anterior to the renal parenchyma since renal rotation is also disturbed. The vascular supply of the ectopic kidney is abnormal, often with several vessels from the distal aorta or iliac vessels.
Signs and Symptoms of Renal Ectopia
Urological complications:
The most common problem is hydronephrosis, followed by vesicoureteral reflux or nephrolithiasis.
Malformations of the genital organs:
In 15%, malformations of the genital organs are present. In women: vagina and uterine malformations. In men: cryptorchidism, duplicate urethra, and hypospadias.
Treatment of Renal Ectopia
Treatment is only necessary for symptoms.
| Supernumerary kidney | Index | Crossed renal ectopia |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
 Deutsche Version: Einfache Nierenektopie
Deutsche Version: Einfache Nierenektopie
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.
New release: The first edition of the Urology Textbook as an e-book—ideal for offline reading and quick reference. With over 1300 pages and hundreds of illustrations, it’s the perfect companion for residents and medical students. After your 7-day trial has ended, you will receive a download link for your exclusive e-book.