You are here: Urology Textbook > Testes > Torsion of testicular appendage
Torsion of Testicular Appendage – Hydatid Torsion
Definition
Torsion of Testicular Appendage is the rotation of the testicular appendix (hydatid of Morgagni) around its pedicle, leading to hemorrhagic necrosis.
Signs and Symptoms of Hydatid Torsion
- Testicular pain
- Edema of the scrotum
- Blue dot sign: the hemorrhagic infarcted appendix testis is visible through the scrotum
| Do you want to see the illustration? Please support this website with a Steady membership. In return, you will get access to all images and eliminate the advertisements. Please note: some medical illustrations in urology can be disturbing, shocking, or disgusting for non-specialists. Click here for more information. |
Diagnostic Workup
Imaging
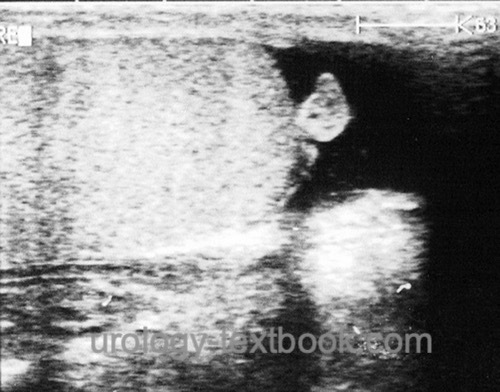
Doppler ultrasonography of the testis: signs for torsion of testicular appendage are a mild hydrocele and an enlarged testicular appendix [fig. ultrasonography of hydatid torsion ] and evidence of testicular blood flow. The reliable differentiation between testicular torsion and torsion of the testicular appendage can be difficult; surgical exploration may be necessary.
 |
Treatment of Hydatid torsion
In principle, the torsion of testicular appendage is treated conservatively with analgesics. In the case of surgical exploration, the testicular appendage is removed after coagulation of the basis.
| Testicular torsion | Index | Varicocele |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
C. Radmayr, G. Bogaert, H. S. Dogan, and S. Tekgül, “EAU Guidelines: Paediatric Urology.” [Online]. Available: https://uroweb.org/guidelines/paediatric-urology/
 Deutsche Version: Hydatidentorsion
Deutsche Version: Hydatidentorsion
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.
New release: The first edition of the Urology Textbook as a Kindle e-book on Amazon—ideal for offline reading and quick reference. With over 1300 pages and hundreds of illustrations, it’s the perfect companion for residents and medical students.