You are here: Urology Textbook > Ureters > Ureter injury
Diagnosis and Treatment of Ureteral Injury and Ureter Trauma
Definition of Ureteral Injury
Ureteral injury is rare and usually caused by penetrating trauma (gunshot or stab wounds). Another mechanism of injury is ureteral tearing due to deceleration trauma (Elliott and McAninch, 2003) (Elliott and McAninch, 2006). EAU Guidelines: Urological Trauma.
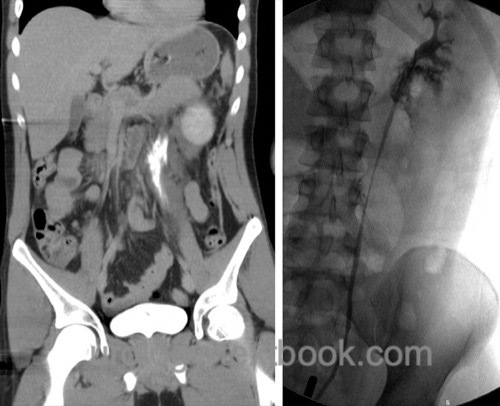 |
Classification of Ureteral Injury
Classification of ureteral injuries according to AAST, advance one grade for bilateral injuries:
- Grade I: hematoma without devascularization
- Grade II: laceration with under 50% transection
- Grade III: laceration with over 50% transection
- Grade IV: laceration with complete transection and less than 2 cm devascularization
- Grade V: laceration or avulsion with more than 2 cm devascularization
Signs and Symptoms of Ureter Injury
The mechanism of injury usually dominates the symptoms of ureteral injury. Additional signs of ureter trauma are abdominal pain, fever, upper urinary tract obstruction, urinoma, hematuria, peritonitis, or urine secretion via the wound.
Diagnostic Workup in Suspected Ureteral Injury
- Abdominal and renal sonography
- Intravenous urography, or better an abdominal computed tomography
- Cystoscopy, retrograde pyelography, and ureteroscopy, if endoscopic treatment is deemed possible
Treatment of Ureteral Injury
Minor ureteral injuries can be managed with endoscopic treatment (Insertion of a ureteral stent, percutaneous nephrostomy). Surgical treatment is necessary for significant ureteral injury (suture repair, ureteroureterostomy, ureteral reimplantation with psoas hitch or Boari flap, transureteroureterostomy or ureteral reimplantation) or long-segment ureteral stricture.
| Extrarenal calyces | Index | Iatrogenic injury |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
EAU Guidelines: Urological Trauma
Elliott und McAninch 2003 ELLIOTT, S. P. ; MCANINCH, J. W.: Ureteral injuries from external violence: the 25-year experience at San Francisco General Hospital.In: J Urol
170 (2003), Nr. 4 Pt 1, S. 1213–6
Elliott, S. P. & McAninch, J. W. Ureteral injuries: external and iatrogenic
Urol Clin North Am, 2006, 33, 55-66, vi
Preston 2000 PRESTON, J. M.: Iatrogenic ureteric injury: common medicolegal pitfalls.
In: BJU Int
86 (2000), Nr. 3, S. 313–7
 Deutsche Version: Traumatische und iatrogene Verletzung des Harnleiters
Deutsche Version: Traumatische und iatrogene Verletzung des Harnleiters