You are here: Urology Textbook > Ureters > Ureteritis cystica
Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment of Ureteritis Cystica
Definition of Ureteritis Cystica
Ureteritis cystica is a rare urothelial inflammatory response leading to vesicles of the ureteral mucosa [fig. ureteritis cystica].
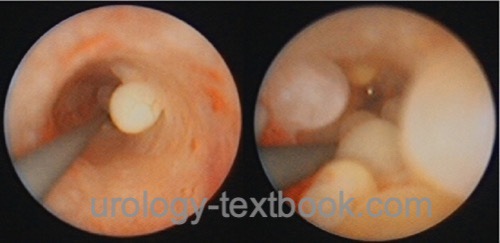 |
Etiology and Pathology
Ureteritis cystica is an inflammatory reaction of the urothelium to infection or mechanical irritation (e.g., nephrolithiasis). The reaction forms subepithelial vesicles of 1 mm to 2 cm in size (von Brunn nests). The vesicles have an epithelial lining and an inflammatory infiltrate around the cysts, filled with protein-rich liquid.
Signs and Symptoms of Ureteritis Cystica
Ureteritis cystica is usually without any complaints. Possible symptoms are hematuria, urinary obstruction with flank pain, urinary tract infection, or symptoms due to nephrolithiasis.
Diagnostic Workup
- Ultrasound: Hydronephrosis?
- Intravenous or retrograde pyelogram: multiple, round, well-defined, small filling defects of the ureteral wall.
- Ureteroscopy with biopsies: only necessary when in doubt to confirm the diagnosis.
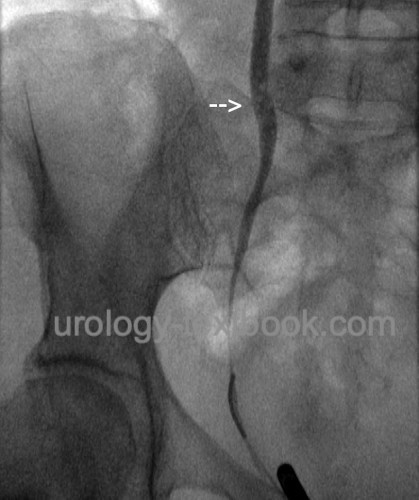 |
Treatment of Ureteritis Cystica
Ureteritis cystica requires no treatment, it will resolve after treating underlying diseases, e.g., antibiotic treatment of UTI or stone therapy. Destruction of the vesicles by ureteroscopy is an option in case of urinary obstruction.
| Retroperitoneal fibrosis | Index | Upper tract urothelial carcinoma |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
M. J. Poturalski, A. S. Purysko, and B. R. Herts, “Ureteritis cystica.,” J. Urol, vol. 193, no. 4, pp. 1379–1380, 2015.
 Deutsche Version: Ureteritis cystica
Deutsche Version: Ureteritis cystica