You are here: Urology Textbook > Surgery (procedures) > Spermatocelectomy
Spermatocelectomy: Surgery for Spermatoceles
Indication for a Spermatocelectomy
Symptomatic spermatoceles: large size or pain.
| Do you want to see the illustration? Please support this website with a Steady membership. In return, you will get access to all images and eliminate the advertisements. Please note: some medical illustrations in urology can be disturbing, shocking, or disgusting for non-specialists. Click here for more information. |
Contraindications to Spermatocelectomy
Coagulation disorders, local skin infections, significant comorbidity with an increased risk for surgery. Operations of the epididymis usually lead to the closure of the epididymal duct. Spermatocelectomy should not be performed, if fertility is an issue.
Preoperative Patient Preparation
- Patient positioning: supine position
- General, spinal, or local anesthesia
- Perioperative antibiotic prophylaxis
Spermatocelectomy: Surgical Technique
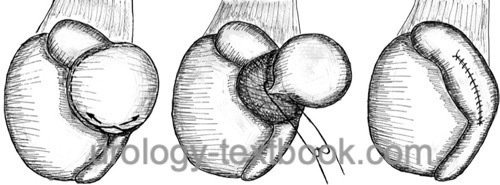 |
- Approach the testis with a scrotal incision.
- Incise the visceral tunica vaginalis covering the spermatocele.
- Incise the visceral tunica vaginalis covering the spermatocele.
- Circularly dissect the spermatocele without damaging the surrounding epididymal tissue. Ligate the basis of the spermatocele.
- Close the visceral tunica vaginalis with a running suture Vicryl 4-0. Consider a closed suction drain after extensive dissection or bleeding diasthesis.
- Close the parietal tunica vaginalis and subcutis (Tunica dartos) with a running suture (Vicryl 3-0). Skin sutures.
| Do you want to see the illustration? Please support this website with a Steady membership. In return, you will get access to all images and eliminate the advertisements. Please note: some medical illustrations in urology can be disturbing, shocking, or disgusting for non-specialists. Click here for more information. |
| Do you want to see the illustration? Please support this website with a Steady membership. In return, you will get access to all images and eliminate the advertisements. Please note: some medical illustrations in urology can be disturbing, shocking, or disgusting for non-specialists. Click here for more information. |
| Do you want to see the illustration? Please support this website with a Steady membership. In return, you will get access to all images and eliminate the advertisements. Please note: some medical illustrations in urology can be disturbing, shocking, or disgusting for non-specialists. Click here for more information. |
Complications of Spermatocelectomy
- Bleeding and hematoma (up to 10%)
- Infection (3-5%)
- Recurrence of spermatocele, formation of hydrocele
- Sperm granuloma, Obstruction of the epididymal duct with infertility.
- Chronic pain
- Testicular atrophy due to vascular injury is rare.
| Hydrocelectomy | Index | Vasectomy |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
J. A. Smith, S. S. Howards, G. M. Preminger, and R. R. Dmochowski, Hinman’s Atlas of Urologic Surgery Revised Reprint. Elsevier, 2019.
Swartz MA, Morgan TM, Krieger JN. Complications of scrotal surgery for benign conditions. Urology. 2007 Apr;69(4):616-9. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2007.01.004.
 Deutsche Version: Operative Therapie der Spermatozele
Deutsche Version: Operative Therapie der Spermatozele
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.
New release: The first edition of the Urology Textbook as an e-book—ideal for offline reading and quick reference. With over 1300 pages and hundreds of illustrations, it’s the perfect companion for residents and medical students. After your 7-day trial has ended, you will receive a download link for your exclusive e-book.