You are here: Urology Textbook > Bladder > Bladder tamponade
Bladder Tamponade: Diagnosis and Treatment
Definition
Bladder tamponade is a bladder filled with blood clots due to hematuria with difficult voiding and risk of urinary retention.
 |
Etiology of Bladder Tamponade:
- Iatrogen: after urologic surgery (TURB, TURP, partial nephrectomy, PNL).
- Diseases: kidney cancer, bladder cancer or prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia, hemorrhagic cystitis, vascular diseases and other causes of hematuria.
- Risk factors: platelet dysfunction, therapy with anticoagulants.
Signs and symptoms:
LUTS, passage of blood clots via the urethra, pelvic pain, urinary retention. In the absence of therapy, bladder rupture with urine extravasation is possible.
Diagnosis:
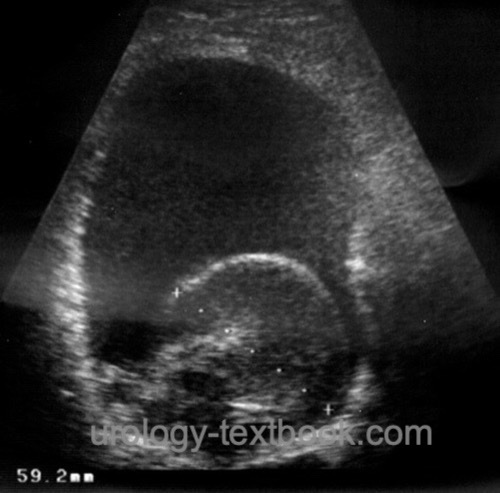
- Ultrasound imaging shows a variable bladder filling with echogenic clots [fig. US of bladder tamponade].
- Blood count and cross-matching for significant bleeding.
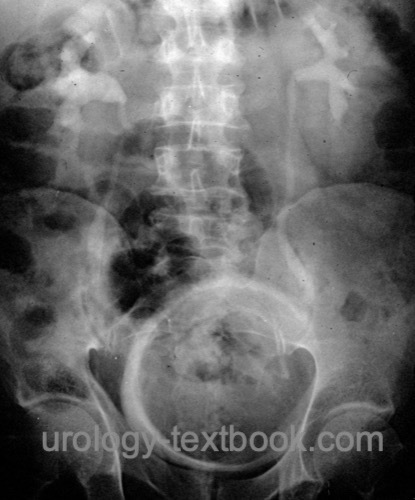
- Further imaging is unnecessary for postoperative bleeding [fig. IVP of bladder tamponade], for unknown hematuria, see diagnostic workup of hematuria.
 |
Treatment of Bladder Tamponade
Acute and low-grade bladder tamponades can be removed with the help of catheters by aspiration with a bladder syringe (preferably via a rigid catheter 20–24 CH). Ensure sufficient analgesia for this painful procedure. After removing the tamponade, an irrigation catheter is inserted, and continuous irrigation is done depending on the intensity of the hematuria.
Pronounced bladder tamponades, especially with active bleeding of the lower urinary tract, necessitate treatment in general anesthesia: aspiration of the tamponade over the shaft of the resectoscope, followed by coagulation of the bleeding area. To treat significant upper urinary tract bleeding, see treatment of the underlying disease.
| Bladder foreing body | Index | Urethral diverticulum |
Index: 1–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
References
 Deutsche Version: Harnblasentamponade
Deutsche Version: Harnblasentamponade
Urology-Textbook.com – Choose the Ad-Free, Professional Resource
This website is designed for physicians and medical professionals. It presents diseases of the genital organs through detailed text and images. Some content may not be suitable for children or sensitive readers. Many illustrations are available exclusively to Steady members. Are you a physician and interested in supporting this project? Join Steady to unlock full access to all images and enjoy an ad-free experience. Try it free for 7 days—no obligation.
New release: The first edition of the Urology Textbook as an e-book—ideal for offline reading and quick reference. With over 1300 pages and hundreds of illustrations, it’s the perfect companion for residents and medical students. After your 7-day trial has ended, you will receive a download link for your exclusive e-book.